
CPC #1: Answer
The procedure performed was bone marrow aspirate and core biopsy. Selected images from the biosy and aspirate are presented below.
 |
 CPC #1: Answer The procedure performed was bone marrow aspirate and core biopsy. Selected images from the biosy and aspirate are presented below. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
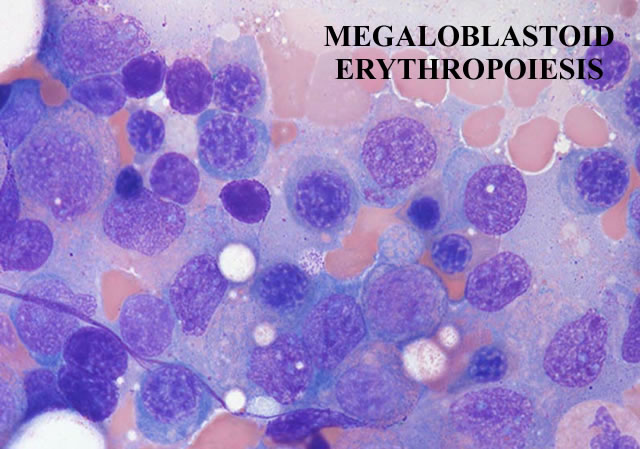
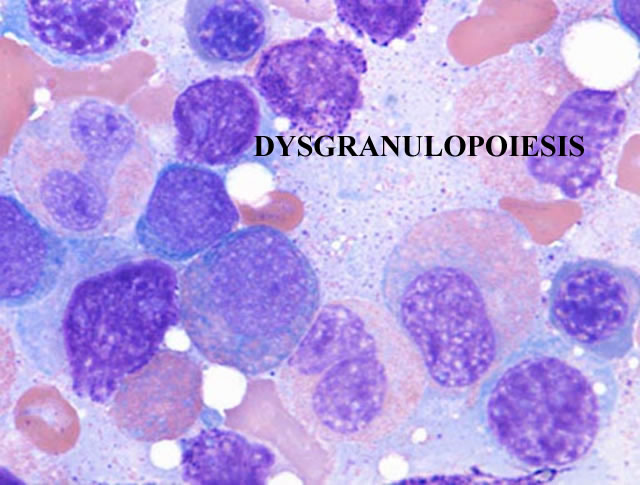
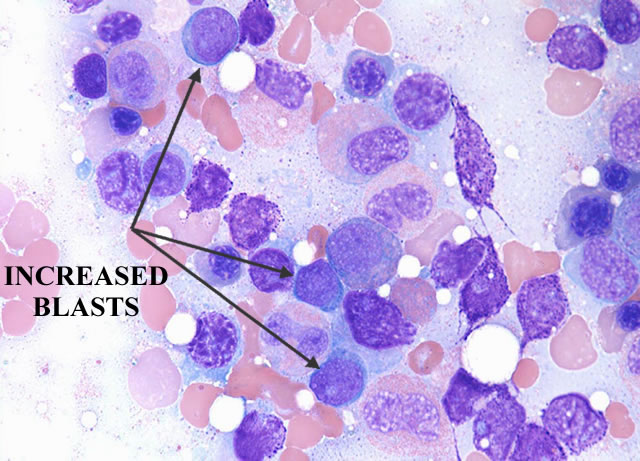
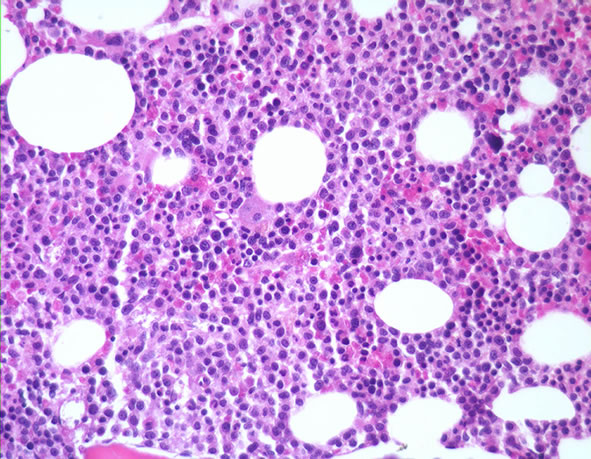
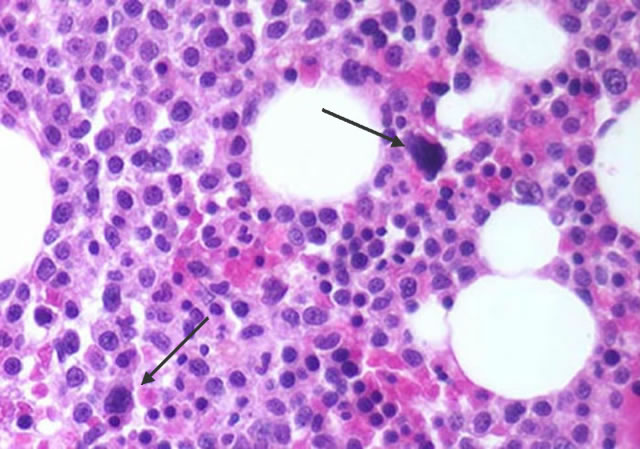
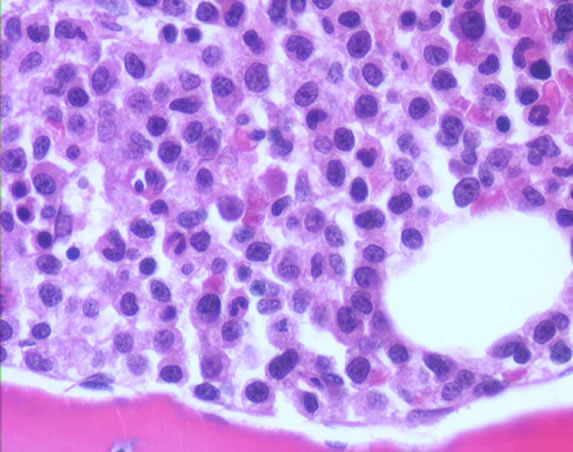
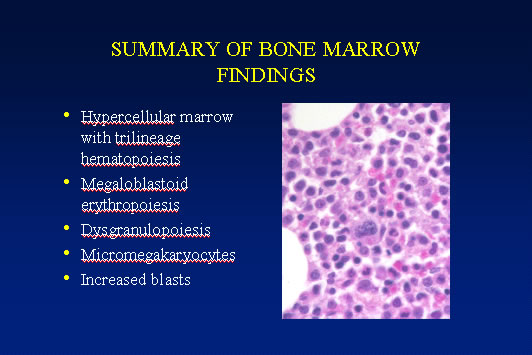
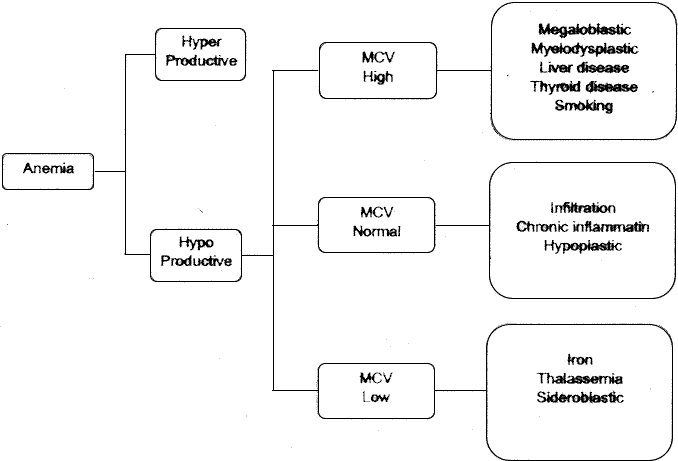
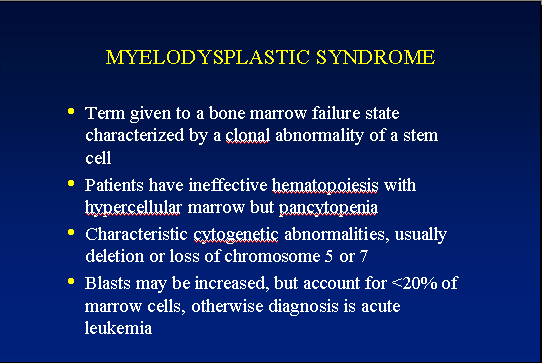
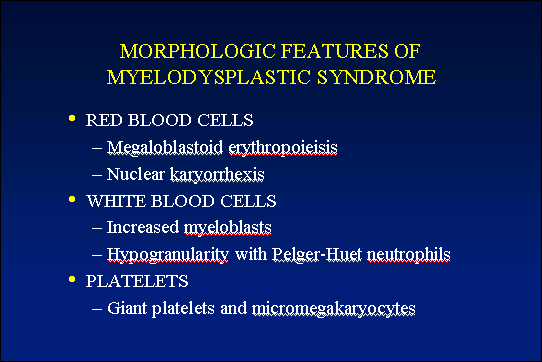
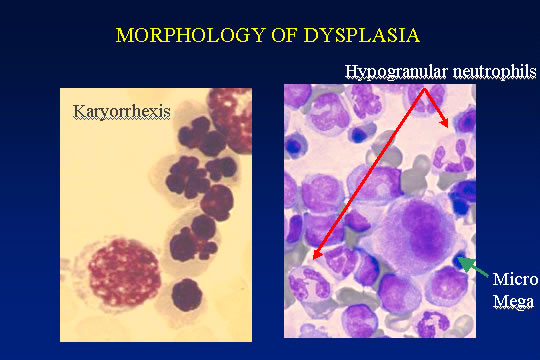
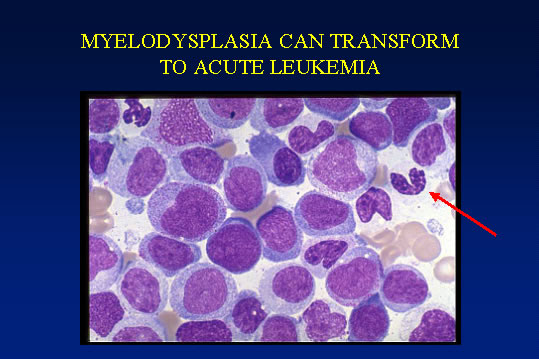
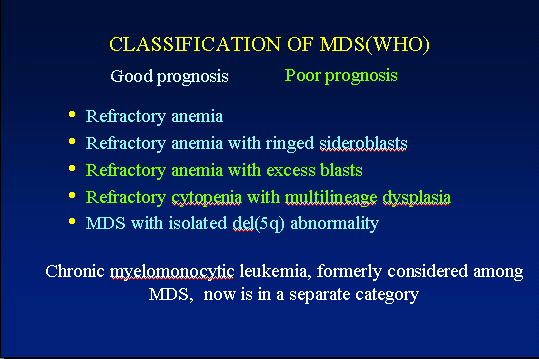
The marrow cellularity was approximately 80%, which is markedly hypercellular for a patient of 80 years of age.† A hypercellular bone marrow in the setting of pancytopenia as was seen in the current case is indicative of ineffective hematopoesis.† Abnormal maturation in each of the three cell lines was identified in the bone marrow.† First, marked megaloblastoid changes were noted within the erythroid lineage.† Second, markedly enlarged megakaryocytes were identified on the core biopsy, which correlates with the giant platelets identified on the smear (see image provided with clinical history).† Finally, there was a marked left shift in myeloid maturation.† There was irregular granulation of the myeloid precursors and mature neutrophils.† Blasts are increased in the bone marrow, but their percentage was less than the 20% required for a diagnosis of acute leukemia.† Rare circulating blasts were identified in the peripheral smear (see image provided with case history).† This constellation of findings is diagnostic of myelodysplastic syndrome: refractory anemia with excess blasts. The current case illustrates the differential diagnostic considerations, which arise when approaching a patient with anemia.† Anemias can be divided into hypo- and hyper-productive ones by analysis the reticulocyte count.† Given the low reticulocyte count in this case in the face of anemia, the patient has a hypoproductive anemia.† Hypoproductive anemias are best classified on the basis of cell size, or mean corpuscular volume (MCV).† Causes of anemia with a normal MCV include bone marrow infiltration, anemia of chronic disease, and aplastic anemia.† Hypoproductive anemias associated with a low MCV are associated with abnormalities of hemoglobin production, such as iron deficiency,thalassemia, and sideroblastic anemias.† Anemias associated with a high MCV include megaloblastic anemias associated with vitamin B-12 or folate deficiency, anemias associated with liver or thyroid disease, smoking, and, finally, myelodysplastic syndromes.† This patientís bone marrow biopsy findings place him within this latter category.† There is no evidence of liver or thyroid disease from the clinical or laboratory findings, and B12 and folate levels were normal.† Hence, the clinical laboratory values pointed toward myelodysplastic syndrome, which was confirmed by the diagnostic bone marrow biopsy. |
 |
||
 |
||
 |
||
 |
||
 |
||
 |
||
| Return to Top | ||
|
|
||